
| 00 | 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 11| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 |
CHEMISTRY

The water molecule.
THE SHADE CONES

The shade cones are zones where the nucleus radiation is weaker.
These zones can capture an electron.
|
|
The nucleus (electron/positron) radiation pattern is similar to that of two antennas fed in quadrature.
There is no on-axis radiation on the right.
However, the nucleus electron/positron system is made of standing waves.
Surprisingly, a convergent radiation replaces the zero radiation on the right:
|
|
Two standing waves sets oscillating at quadrature generate inward waves, hence an attraction effect.
A polarization occurs if both spins are not present, explaining magnetic fields: north and south poles.
Any unmatched electron generates a magnetic field because it is coupled with a proton's positron.
This magnetic field is cancelled if the electron from the opposite spin is present on the opposite side.

Ionic binding: chlorine (left) borrows a electron from the sodium atom, which becomes positive.
The 8-electron external atomic layer is complete on both sides; so the "shade cones" are not involved.
This phenomenon occurs only because of the Coulomb force.
However, the Van der Waals forces may reinforce this binding, producing a salt crystal.

Simple binding.
One electron only can bind two atoms; it must be captured by two shade cones simultaneously.
However, a covalent 2-electron binding involving four shade cones (see below) is stronger.
COVALENT BINDING
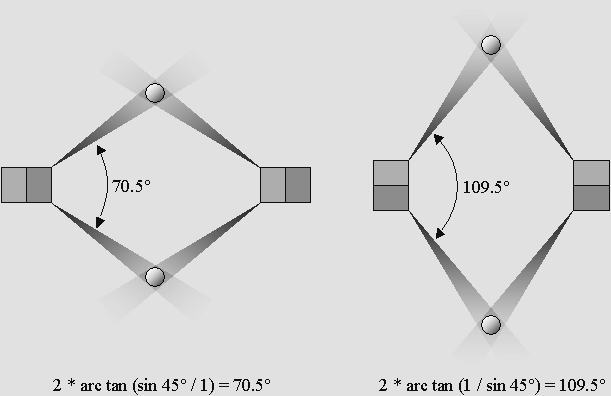
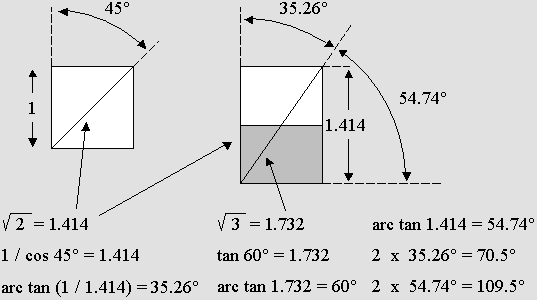
Covalent binding: two atoms containing two unpaired electron (no opposite spin) can share them.
Two binding angles are possible whether the second electron is on the side or on the diagonal.
This 2-pivot structure may induce a hinge effect.
This indicates that diagonal unpaired electrons may more easily produce more dense molecules.

Carbon monoxide.
The oxygen atom (left) is saturated, but two unused shade cones on the right can still bind more atoms.
For example, one more oxygen atom will create CO2, two hydrogen atoms, formaldehyde, etc.
ANY MOLECULE USES CUBICAL GEOMETRY

The water molecule.
The hydrogen atom is an exception in chemistry: its electron is not necessarily captured inside a shade cone.
In any atom, the two internal electrons are located on opposite sides of the nucleus inside magnetic fields.
| 00 | 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 11| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 |
|
|
Bois-des-Filion in Québec. Email Please read this notice. On the Internet since September 2002. Last update October 17, 2008. |